LABICUPER in vineyard, France
Essay
Location: Saint-André de Cubzac and Puy L’Evèque, France.
Crop: Vitis vinifera of the MERLOT (at Saint-André de Cubzac) and MALBEC (at Puy L’Evèque) varieties, grown in randomized blocks of 4 replicates each (one for each treatment). At Saint-André de Cubzac each replicate comprises 12 strains (each block comprises 48 strains). In Puy L’Evèque, each replicate comprises 56 strains (each block comprises 56 strains).
Objective: To comptabilize the content of the nutrient element “copper” and other nutrients analyzed (N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, Zn, B) in the sap flow and in grapevine berries in order to test the effectiveness of an increase in the content of these nutrients in the vegetative body, in terms of copper fertilization.
Witness: Temoin.
Dates: June 2019-July 2019.
Applications: 6 applications (one every week) (5 in the case of the Puy L’Evèque site). Each application with a dose of 2 L/ha of LABICUPER in 100 L/ha of liquid volume before flowering and 150 L/ha after flowering. No other foliar treatment was performed on the trial plots.
The total copper dose in the field with the application of LABICUPER is 0.99 kg copper nutrient/ha and field (for the Saint-André de Cubzac site) and 0.82 kg copper nutrient/ha and field (for the Puy L’Evèque site). The product has 6.8% copper (w/w) and a density of 1.21 kg/L (8.23% copper w/v)
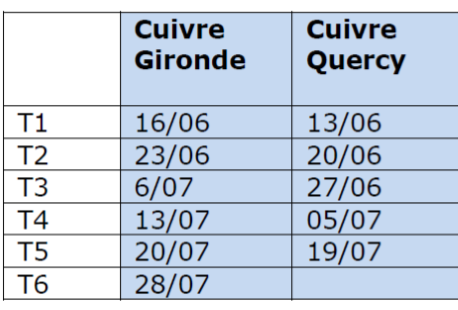
The first application of the treatments at the Saint-André de Cubzac (“GIRONDE”) location took place on June 16, 2019, ending on July 28, 2019 (Table 1). In the locality of Puy L’Evèque (“QUERCY”) the first application was carried out on June 13, 2019, ending on July 19, 2019.
Outline of the test

Results


The results show that the LABICUPER treatment shows a higher copper content in the sap flow compared to the untreated testimony (an increase of 226%) (see Table 1 and Graph 1). As well as an increase in the elements Potassium (K) (an increase of 83%), Iron (Fe) (an increase of 67%), Zinc (Zn) (an increase of 82.4%) and Boron (B) (an increase of 50%).
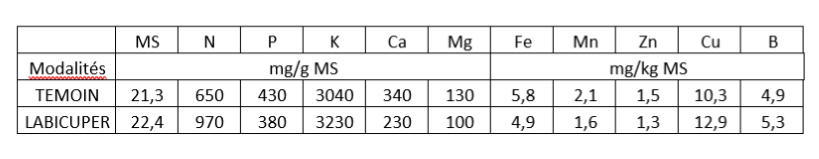
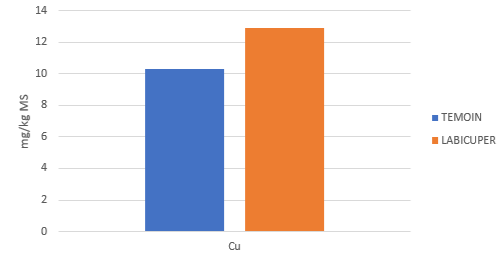
The results show that the LABICUPER treatment presents a higher copper content in the grapevine berry compared to the untreated (an increase of 25.2%)(see Table 2 and Graph 2). As well as an increase in the elements Nitrogen (N) (an increase of 49.2%), Potassium (K) (an increase of 6.25%) and Boron (B) (an increase of 8.16%).
Conclusions
Both sap flow and grapevine berry measurements show that the LABICUPER treated strains at the two locations have a higher copper content than the untreated control (testimony).
The results in sap flow are much higher with respect to the analysis of the different nutrients in grape berries (in the order of 10 times higher in the case of copper, as well as an increase in the other nutrients). The results confirm that the plant responds to the application of the product with a stimulation of the absorption of the different elements described and copper is assimilated in the vascular system of the plant and is available to the plant for its vital functions.
The assimilation of copper in the vine leads to an increase in the content of the elements Nitrogen (N), Potassium (K), Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn) and Boron (B) in the vegetative body.




